

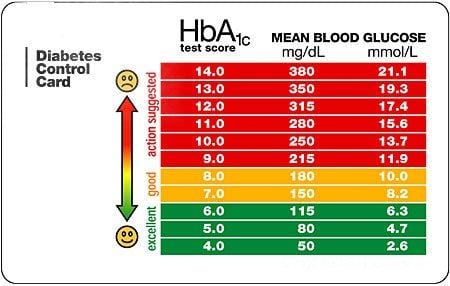
Undergoing the A1C test is straightforward: A healthcare professional takes a blood sample and sends it to a laboratory for testing. The more glucose in a person’s bloodstream, the more hemoglobin is bound to glucose. When glucose enters the blood, it binds to hemoglobin. It helps carry oxygen from the lungs to other tissues. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein in red blood cells. This measurement gives doctors an idea of the person’s average blood glucose levels over the past 2–3 months. If your score is less than 70%, you can return to this section and review the information.The A1C test measures the percentage of red blood cells that have glucose-coated hemoglobin. If your score is over 70% correct, you are doing very well. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. Please choose the single best answer to each question. To find out how much you have learned about Monitoring Your Diabetes, take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. The fructosamine test reflects the average blood sugars only over a 2-3 week period. Unfortunately, the fructosamine test and the A1c are not interchangeable because they are measuring different things. An alternative test to the A1c is a fructosamine test. If your finger-stick blood tests give an average blood sugar that is much higher or lower than your A1c test, ask your doctor if the A1c is the right test for you. For example, if someone has certain type of hemoglobin mutations (variation in the hemoglobin structure), is severely anemic (low red blood cell count), iron deficient or is being treated blood transfusions or medications to increase the production of new red blood cells, the A1c test may not be accurate. Use this chart to view A1c values and comparable blood glucose values: A1cĪ note of caution: the A1c measurement is not always accurate. Talk with your doctor about your A1c goal.For some people with diabetes an A1c goal of less than 6% is appropriate.

As red blood cells live an average of three months, the glycosolated hemoglobin reflects the sugar exposure to the cells over that time. The glucose-hemoglobin unit is called glycosolated hemoglobin.
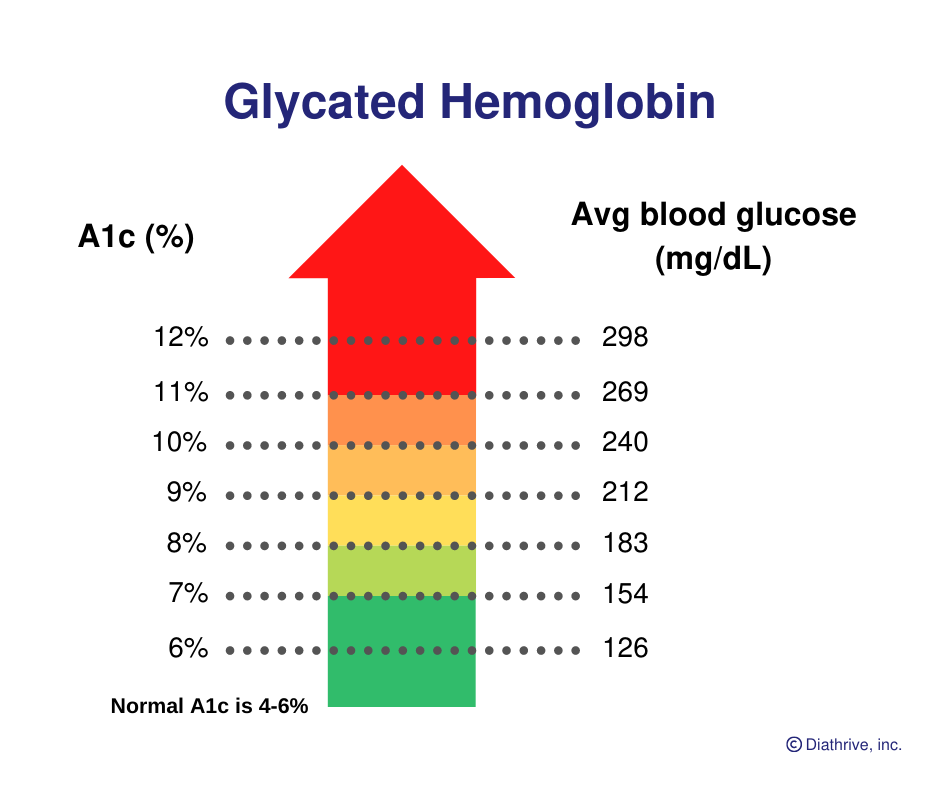
Glucose attaches to hemoglobin the oxygen carrying molecule in red blood cells. Glysolated Hemoglobin (or A1c) is a measure of your average blood glucose control over the previous three months.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
